Huge Canyon Discovered Under Greenland Ice
One of the biggest canyons in the world has been found beneath the ice sheet that smothers most of Greenland.
Scientists are surprised the feature has not been worn away by successive glaciations
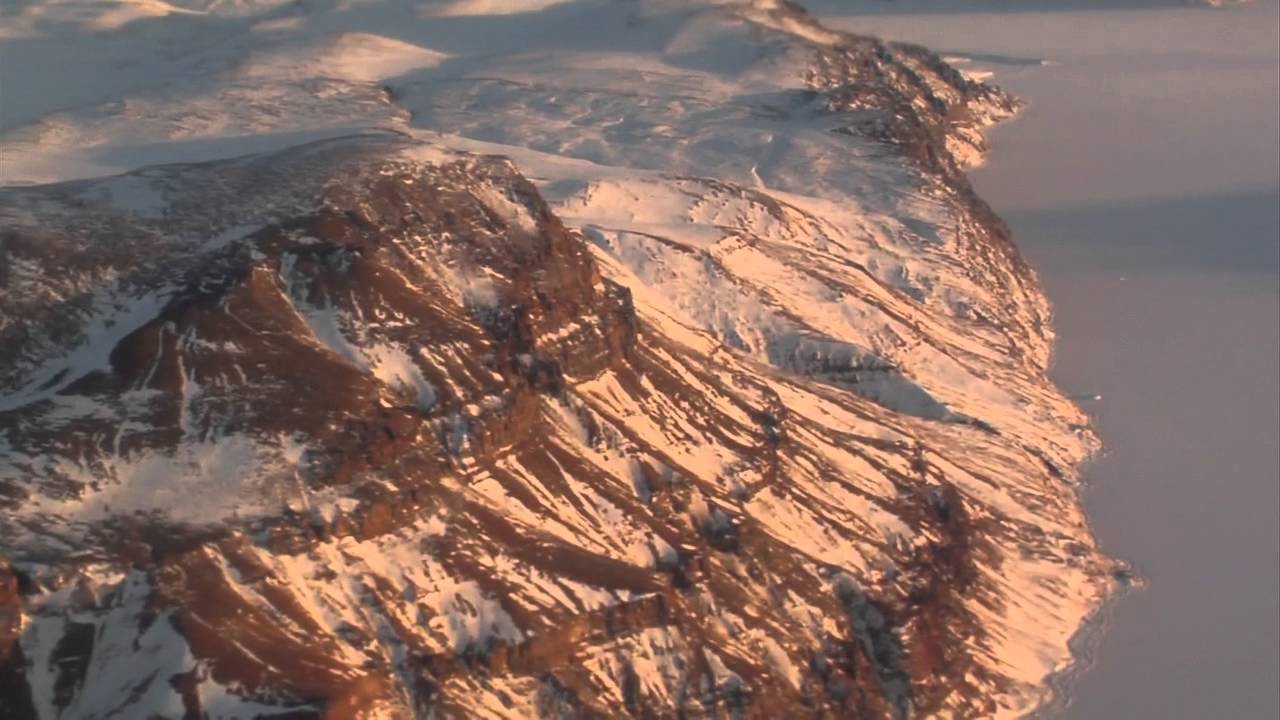
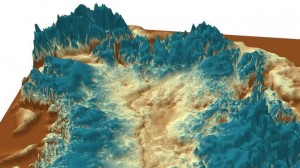
BBC: The canyon – which is 800km long and up to 800m deep – was carved out by a great river more than four million years ago, before the ice arrived. It was discovered by accident as scientists researching climate change mapped Greenland’s bedrock by radar. The British Antarctic Survey said it was remarkable to find so huge a geographical feature previously unseen.
The hidden valley is longer than the Grand Canyon in Arizona. It snakes its way from the centre of Greenland up to the northern coastline and before the ice sheet was formed it would have contained a river gushing into the Arctic Ocean. Now it is packed with ice.
The ice sheet, up to 3km (2 miles) thick, is now so heavy that it makes the island sag in the middle (central Greenland was previously about 500m above sea level, now it is 200m below sea level). The canyon still runs “downhill”, though, and meltwater from the ice sheet seeps out below sea level at the northern end – at a relative trickle, rather than a torrent. Glaciologists think the canyon plays an important role in transporting sub-glacial meltwater produced at the bed towards the ocean.
The canyon was discovered by researchers working on one of the great scientific puzzles – how much will the Greenland ice sheet contribute to sea level rise if, as predicted, the Arctic continues to warm as greenhouse gases increase? They sought the answer with myriad flights using radar to bounce signals back off the bedrock underneath. Ice is transparent to radio waves at certain frequencies.
Studying the data collected mainly by NASA and researchers from the UK and Germany over decades, they were amazed to stumble across the canyon. The lead author, Prof Jonathan Bamber of Bristol University said: “With satellite images instantly available on a mobile phone we could assume that the Earth has been fully mapped, but there’s clearly a lot left to discover. We’re incredibly excited about this – it really is a once-in-a-lifetime discovery to find something on this scale.”
Prof David Vaughan from British Antarctic Survey (Bas) told BBC News: “The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets hide a lot. It’s pretty surprising to find this canyon. Greenland isn’t that big for a canyon of that size, and for it to survive in its pre-glacial form after successive glaciations is quite something.” Prof Vaughan said the canyon would have been partly uncovered at the time of the last interglacial 100,000 years ago. “There’s likely be some sort of bacteria down there – whether it’s viable is a different matter,” he said.
The canyon has never been seen by humans, who didn’t exist four million years ago. If the Greenland ice sheet melts completely it will raise global sea level by 7 metres and swamp many major cities, so hopefully this is one great geographical feature that won’t become a tourist destination.
The study Paleofluvial Mega-Canyon Beneath the Central Greenland Ice Sheet
Abstract
Subglacial topography plays an important role in modulating the distribution and flow of basal water. Where topography predates ice sheet inception, it can also reveal insights into former tectonic and geomorphological processes. Although such associations are known in Antarctica, little consideration has been given to them in Greenland, partly because much of the ice sheet bed is thought to be relatively flat and smooth. Here, we present evidence from ice-penetrating radar data for a 750-km-long subglacial canyon in northern Greenland that is likely to have influenced basal water flow from the ice sheet interior to the margin. We suggest that the mega-canyon predates ice sheet inception and will have influenced basal hydrology in Greenland over past glacial cycles.
This new discovery could offer new possibilities for obtaining climate proxies from Greenland ice cores and maybe reveal methane deposits.
Related ‘Massive’ reservoir of melt water found under Greenland ice