It Doesn’t Matter If We Never Run Out of Oil: We Won’t Want to Burn It Anymore
Like whale oil in the 1860s, oil today has become uncompetitive — even at low prices — and that will only become truer with time.
Amory B. Lovins / The Atlantic: Charles C. Mann is a great storyteller, but “What If We Never Run Out of Oil?” tells the wrong story and is marred by bloopers.
Mann’s story is entirely about quantity of supply, not price nor the more-efficient use it encourages. Yet mainstream analysts see “peak oil” emerging not in supply but in demand: OECD oil use peaked in 2005, U.S. gasoline use peaked in 2007, and some analysts think world oil use may peak in this decade. Why? Modern technologies to save or displace oil cost far less than oil. The 2011 study Reinventing Fire found that an uncompromised, oil-free U.S. automobile fleet would cost $18 per saved barrel, rising to about $25 per barrel for all transportation. That’s manyfold cheaper than any source of oil Mann describes, yet he doesn’t discuss efficient use or price. That’s the big story: Like whale oil in the 1860s, oil has become uncompetitive even at low prices, long before becoming unavailable even at high prices.
This comparison doesn’t even consider hidden or external costs. Just the economic and military costs of U.S. oil dependence, if paid at the pump rather than through taxes and reduced wealth, would triple the price of oil — plus any costs to health, safety, environment, climate, global stability and development, or our nation’s independence and reputation.
Climate risk alone makes it dangerous to burn most known oil and other fossil-fuel reserves (conventional and unconventional), so the more carbon-intensive and costly new fuel sources that Mann describes are even more unburnable. Ways to get more oil or gas we don’t need, can’t afford, and can’t safely burn will hardly define the future of our energy mix.
Mann’s article contains many errors, starting with the article’s title. Mann’s featured methane hydrates yield natural gas, not “oil.” Oil and gas differ sharply and are often not fungible. Mann oddly uses “petroleum” to mean both oil and gas, but to the U.S. Energy Information Administration and most authorities, petroleum is a liquid.
Mann states “a basic truth: Economic growth and energy use have marched in lockstep for generations.” He supports this claim by a single comparison for the whole world (mixing developing with industrialized economies), for all forms of energy (diluting oil and gas with cheap coal and hydropower), during 1900-2000 (for nearly three-fourths of which real oil and gas prices were the lowest and most stable in history). Actually, Mann’s “lockstep” broke with the first oil price shock 40 years ago. The U.S. used 62 percent less oil and gas per dollar of real GDP in 2012 than in 1973. When the U.S. last paid serious attention to oil, in 1977-85, oil used per dollar of GDP fell at an average rate of 5.2 percent per year. Today’s oil-saving technologies are better and cheaper.
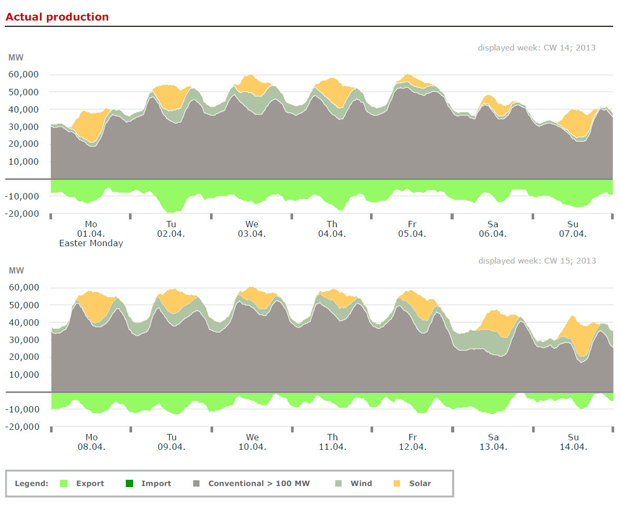
Mann says Germany is burning more coal and “steadily” emitting more carbon as it shifts to renewables. In fact, Germany’s 2011-12 uptick in coal-fired power generation, offsetting pricier gas, is a blip on a solid downward trend. And despite economic growth, German carbon emissions fell 2.8 percent in 2011; in 2012 they rose 1.6 percent due to a cold winter but fell after weather adjustment. Germany’s greenhouse-gas emissions in 2012 were 25.5 percent below those of 1990, meeting its Kyoto obligation.
Mann asserts that “Although the cost of renewable energy is falling rapidly, it is not yet equivalent to the cost of energy from fossil fuels.” In fact, new utility-scale solar power underbid efficient new gas-fired plants in California’s spring 2011 auction; since then, solar got cheaper and gas costlier, with German solar systems averaging half the installed cost of U.S. ones. And new Windbelt wind farms in 2011-12 sold their output for for $25-40/MWh, averaging $32/MWh — often competitive despite nonrenewable competitors’ often larger subsidies, and without counting wind’s value in hedging against volatile gas prices. Gas’s price volatility, which efficiency and most renewables lack, also makes fracked gas cost about twice as much as commonly supposed, even if its roughly eight kinds of major risks and uncertainties are all satisfactorily resolved.
A man in Germany examines the solar panels on his roof, making power he can resell at an excellent financial return. Germany recently installed more solar cells in a single month than the United States did in all that year. (Reuters)
Most bizarre is Mann’s claim that mostly-renewable electricity would cause brownouts and factory shutdowns (which he says Germany “is already facing”) and require massive electrical storage and transcontinental transmission. He even says “many utility-energy engineers predict” that when “renewables supply 20 to 30 percent of all electricity, … the system will no longer be able to balance supply and demand.” Thanks to proven modern utility practice, none of that is true — and far from our needing to burn more and more gas to bridge to a distant renewable future, renewables are quickly scaling well beyond his mythical limit.
Germany was 23 percent renewable-powered in 2012 (doubled in six years), with two states in 2011 at 45 percent and 58 percent, while German power reliability rose to the highest in the European Union. Denmark was 41 percent renewable-powered in 2012 (peaking at 80 percent); Portugal, 45 percent (peaking at 100 percent the previous year, and rising to 70 percent for the whole first quarter of 2013). Earlier this year, Spain briefly achieved 61 percent renewable power and Germany 70 percent, while Texas neared 30 percent wind power on some days and the U.S. utility Xcel reached 57 percent for an hour. And as for the future, California’s 33-percent-renewable and Denmark’s 50-percent-windpower goals for renewable power by 2020 are on track. Germany’s 35-percent-renewable-power goal for 2020 is ahead of schedule, and eight countries’ and 41 cities’ 100-percent-renewable-power (or even -energy) goals look both practical and profitable.
Thus, even if oil and electricity were linked — they’re less than 1 percent linked in the U.S., less than 5 percent globally — Mann’s claims that renewables can’t reliably supply over 20-30 percent of electricity and are too slow to avert rising “petroleum”-burning are belied by realities on the ground.
Finally, Mann’s reply to Chris Nelder’s comments removes any doubt that Mann’s misunderstandings of the modern electricity system are fundamental. First, he confuses the storage that a single solar-powered house needs to work without the grid (a rare case) with how the grid itself shifts to largely or wholly renewable supply. That doesn’t require backing up each solar array or wind machine with batteries, which do become costly if one uses electricity inefficiently. Rather, a diverse portfolio of wind and photovoltaics (a) sited in different places so they experience different conditions and (b) of different kinds (sunny calm days are bad for wind but good for solar) is integrated with (c) the many other kinds of renewables, nearly all of which are “dispatchable” (available whenever needed), with (d) unobtrusively flexible demand, and with (e) distributed storage, mainly ice-storage air-conditioning and smart bidirectional electric-car charging. If necessary, (f) existing, especially fast-responding, gas-fired generators can fill any gaps, but that’s not always necessary.
The U.S. and European examples above — now including Spain‘s 52-percent-renewable electricity supply for all March and 54 percent for all April (when the mix included 25 percent hydro, 22 percent wind, 5 percent solar) — were achieved not by bulk storage but by deftly choreographing the operation of utilities’ existing assets, using wind and sun to back out fossil fuels. In this way, San Diego Gas & Electric expects its fossil-fueled generation on sunny afternoons (when electricity is most scarce and valuable) to drop to zero within the next few years as solar power burgeons.
But we can go further. For example, my colleagues’ hourly simulations show that after efficiency gains that the National Academies consider highly profitable, the isolated Texas grid (ERCOT) can meet demand reliably for every hour of the year 2050 with 100 percent renewables by using just options (a) through (e) — using no fossil-fueled or nuclear power, no bulk electrical storage, and with only 5 percent of renewable generation left over. Reinventing Fire‘s 80-percent-renewable, 50-percent-distributed, highly resilient 2050 “Transform” scenario would need bulk storage only 5 percent as big as its renewable capacity and would cost essentially the same as business-as-usual, but would make cascading blackouts impossible and mitigate the grid’s six other big risks. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s equally rigorous REFS study showed how an 80 to 90 percent centralized-renewable U.S. grid could run reliably, with reasonable economics, and again with relatively little storage. Indeed, high-renewables futures may need less storage and backup than utilities have already bought (or would need to buy) to manage the intermittence of their big thermal power stations, which fail far less gracefully than a sensible renewable portfolio.
It also doesn’t matter that there’s currently “no way for power from places like the southwest, with plenty of sun, to flow to places like the northeast, which lack sun,” because that’s unnecessary and uneconomic. The cloudiest parts of the U.S. have at least half as much annual sun as the sunniest. New Jersey is now the Number 2 solar-powered state, after California, with ample sunshine to make a good business case. But the sun also isn’t the only renewable source: There’s wind, small hydro, geothermal, waste and biogas, tidal, wave, and more. Each region has its own mix. NREL’s REFS study, Reinventing Fire, and others confirm that each region of the United States has an abundant and cost-effective range of renewable power choices. But nearer is often better: for example, Great Lakes wind rivals the Dakotas for powering Chicago, while offshore windpower could power the Northeast (though one would actually use a diversified portfolio).
The emerging regional strategy looks cheaper, easier, and more secure than shipping renewable power cross-country. Indeed, new transmission will increasingly have to compete with efficient use and distributed generation, and often won’t be able to. And distributed renewable power plus “microgrid” architecture is the best if not the only way to make the grid highly resilient, enhancing our national security at essentially no extra cost.
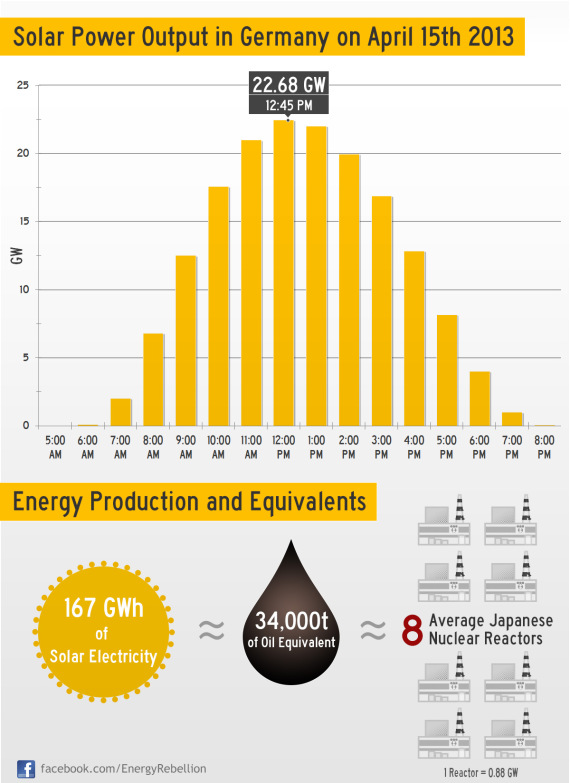
Solar Power Record In Germany — 22.68 GW — Infographic
Clean Technica: On Monday, the 15th of April, 2013, the approximate 1.3 million solar power systems in Germany set a new domestic/world record by reaching a peak power output of 22.68 GW at noon.
The New Normal
This new record is almost 0.5 GW above the “old” record of 22.2 GW, which was set on May 25th, 2012. Allthough I love celebrating all solar records, the biggest news might be that “just” 22.68 GW is apparently no longer newsworthy in Germany,because above 15-20 GW of solar have become a regularity.
During the first two weeks of April, solar surpassed the 20 GW mark on several occasions and made a meaningful contribution to the domestic power supply on every single day. For everybody remotely familiar with German or Central European weather conditions, it’s needless to say that it wasn’t all sunshine & cloudless skies in April.
Since solar panels last for 25+ years and have almost no marginal costs, I like to use the opportunity to mention the fact that whatever might happen in policy in the coming years, those yellow areas of the electricity market will remain liberated* from the external effects caused by conventional electricity production for at least one generation. (*To use a slightly more energy revolutionary sort of language)
So, lets celebrate the new solar world record of 22.68 GW of solar power on a national grid, despite its relative “mediocrity,” with a little infographic!
In case you are wondering: The equivalents mentioned in the infographic were chosen for the Japanese “market” (for solar and ideas).
- The 167 GWh of solar electricity provided a little more than 12% of the total German electricity consumption on a typical Monday in April (presuming that consumption hasn’t changed too much since last year).
- The 34,000 tons of oil are calculated by considering a thermal power plant efficency of 42%, meaning that for each kWh of electricity you got to burn 2.4 kWh of oil. (42% is the average for Japanese oil-fired power stations that usually provided peakload electricity before, and now even more so after, the Fukushima nuclear accident.)
- The number of nuclear reactors refers to each one running for 24 hours straight. The comparison is intended to show that distributed solar can make a big impact and doesn’t need years to build. I am aware that comparing clean peak-load solar operating in the renewable energy paradigm with old-school baseload nuclear is relatively pointless.
About the Author: CLIMATE STATE
POPULAR
COMMENTS
- The risk with the path to a hothouse Earth | Climate State on Climate Tipping Points Existential Threat to Our Life Support Systems
- Robert Schreib on Electricity generation prices may increase by as much as 50% if only based on coal and gas
- Robert Schreib on China made a historic commitment to reduce its emissions of greenhouse gases
- Lee Nikki on COP30: Climate Summit 2025 – Intro Climate Action Event
- Hollie Bailey on Leaders doubled down on fossil fuels after promising to reduce climate pollution